Optical Brightening Agent
Brighton D
Brighton D has an outstanding affinity and is highly suitable for fluorescent whitening in the furnish at slightly acid or neutral ph. Broadly not affected by cationic substance. It can readily be used with mechanical pulp or secondary fiber.
Product Property
- C.I. No. : 113
- CAS No : 4193-55-9
- Chemical name : Benzenesulfonic acid,2,2′-(1,2-ethenediyl)bis[5-[[4-[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-6-( -(phenylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]-,sodium salt (1:2)
Chemical Structure
- Composition: Stilbene
- Disulphonic Derivative
- Physical Appereance: Brownish yellow to Reddish Yellow
- Ionic Character: Anionic
- Ph: 9.5-10.0
- Specific Gravity (gm/ml): 1.11-1.14
- Shade: Neutral Shade
- Viscosity: Max. 50mPa.s at 25ºC
- Solubility: Miscible
- Brightning Effect: Confirms to std equal to product of same chemistry, tolerance limit CIE difference ± 1
Property
- Sufficient fiber affinity
- Good alkali stability
- Little acid/alum stability
- Suitable for using in the condition of PH value 5-13
Brighton T
Brighton T is a versatile tetrasulpho type optical whitening agent. It is used in wet ends, size presses, and coating applications on paper. Brighton T is a versatile tetrasulpho type optical whitening agent. It is used in wet end, size press, and coating applications in paper.
Product Property
- C.I. No. : 220
- CAS No : 41098-56-0
- Chemical name : 1,4-Benzenedisulfonicacid,2,2′-[1,2-ethenediylbis[(3-sulfo-4,1- phenylene)imino[6-(diethylamino)-1,3,5-triazine-4,2-diyl]imino]]bis-,sodium salt
Chemical Structure
- Composition: Stilbene Tetrasulphonic Derivative
- Physical Appereance: Light yellow to Brownish Yellow
- Ionic Character: Anionic
- Ph: 9.5-10.0
- Specific Gravity (gm/ml): 1.10-1.14
- Shade: Neutral Shade
- Viscosity: >50mPa.s
- Solubility: Miscible
- Brightening Effect: Confirms to std equal to the product of same chemistry, tolerance limit CIE difference ± 1
Brighton H
Brighton H Liquid is a hexa sulphonic type florescent brightening agent which is used in surface coating and size press liquor in paper industry. It gives best whiteness and brightness in treated papers. It can used in alkali, neutral and acidic condition so, there is no bound of Ph for this product.
Product Property
- C.I. No. : 264
- CAS No : 68971-49-3
- Chemical name : 1,4-Benzenedisulfonicacid,2,2′-[1,2-ethenediylbis[(3-sulfo-4,1- -phenylene)imino[6-[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazine-4,2- -diyl]imino]]bis-,hexasodium salt
Chemical Structure
- Composition : Stilbene Tetrasulphonic Derivative
- Physical Appereance : Light yellow to Brownish Yellow
- Ionic Character : Anionic
- Ph : 9 – 11
- Specific Gravity (gm/ml) : 1.0 – 1.12
- Shade : Slightly Reddish tone on coating application.
- Viscosity : Lower than 75 mPas
- Solubility : Miscible
- Brightning Effect : Confirms to std equal of same chemistry, tolerance limit Tappi difference ±1
Property
- Excellent white performance, especially suitable for achieving high whiteness in coating and sizing process.
- Good acid stability, it can achieve high whiteness in low PH value situation.
- Good light fastness.
- Fully diluted in water, suitable for continuous addition.
- Suitable for using in the condition of PH value 1-13.
Defoaming Agents
 Function: To cause foam bubbles to coalesce to the point where they are large enough to float harmlessly to the water surface and break.
DEFOAMING EFFICIENCY AT.015KPT
Function: To cause foam bubbles to coalesce to the point where they are large enough to float harmlessly to the water surface and break.
DEFOAMING EFFICIENCY AT.015KPT
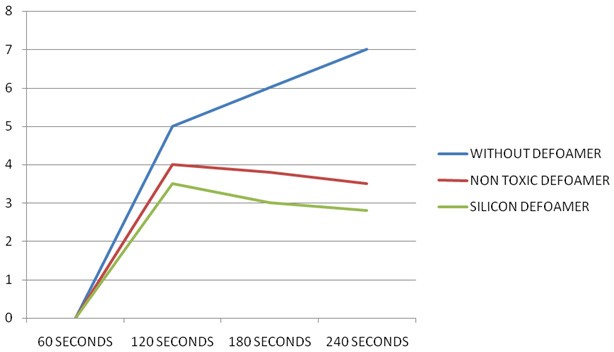 Figure 1: EFFICIENCY OF ABSTRACT DEFOAMER
Below the table has been provided by one of our customers of Paper Mill while they were making a Laboratory Test of our Non Toxic Defoamer
Figure 1: EFFICIENCY OF ABSTRACT DEFOAMER
Below the table has been provided by one of our customers of Paper Mill while they were making a Laboratory Test of our Non Toxic Defoamer
| Time Second | HEIGHT OF FOAM | Other Defoamer | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | Abstract non Toxidefoamer | ||
| 0 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| 10 | 420 | 320 | 400 |
| 20 | 530 | 330 | 520 |
| 30 | 580 | 330 | 540 |
| 40 | 620 | 330 | 600 |
| 50 | 700 | 330 | 680 |
| 60 | 790 | 330 | 700 |
| Defoaming Efficiency % | – | 58.22 | 11.39 |
| Product Name | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Abstract Non Toxic Defoamer (Ntd) | White water defoaming during formation of paper sheet |
|
| Abstract Silicon Defoamer (SD) | For wood bamboo, rice-wheat-straw, bagasse, and other type of pulp making |
|
| Abstract Af Paper Coating Defoamer | For paper coating |
|
Deinking Solutions
Deinking essentially involves three steps:
- Detachment of ink from fibers
- Removal of detached ink from fibers
- Water clarification for reuse and disposal of removed ink and contaminants.
Deinking is the industrial process of removing printing ink from paper fibers of recycled paper to make deinked pulp.
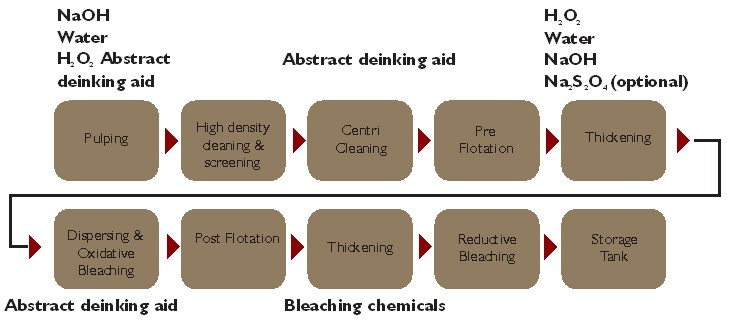
The key in the deinking process is the ability to detach ink from the fibers. This is achieved by a combination of mechanical action and chemical means. In Europe the most common process is froth flotation deinking.
Deinking chemicals are generally added to the pulper. During pulping the recovered paper is slushed into a pulp at high consistency. The combination of chemical and mechanical action is favourable. Additionally, by dosing early in the process to the pulper the reaction time is increased as well as the more effective dosage of some chemicals as the result of a high consistency. Figure 1 shows a schematic layout of a typical deinking process for the production of pulp for graphical grade paper. Often all deinking chemicals are added to the pulper, but sometimes some or all of the deinking aid can also be added to the flotation cell.
Benefits of abstract deinking:
- Improve Ink Removal
- Improve Pulp Quality
- Lowers Bleaching Costs
- Most effective in Deinking plants that use old newsprint and old magazine waste furnish.
- Highly concentrated effective deinking agent
- Excellent collector chemical for flotation deinking
- Enables the leading white grade plants to achieve deinked pulp of quality equal to virgin pulp in brightness and dirt.
- Cost effective
- Lead to higher brightness
- Lower dirt counts in finished paper
- Improve pulp Bleachability & Brightness level
- Lowe dirt count
- Reduce or eliminate the use of certain chemicals
- Environment friendly
- Enhances the removal of ink particles
- Very efficient even at low dosage levels
| Product Name | Benefits | Addition Rate/Ton | Chemistry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abstract D | Excellent Removal of Ink | 0.4 – 0.5 % | A Sodium Salt Of Selected Fatty Acid Based |
| Abstract HD | Enhanced collector chemical for flotation deinking | 0.4 – 0.5 % | A Sodium Soap Of Cps Plus A Synergistic Additive |
| Abstract Di Hc Liq | Excellent cost effective In The Removal of Ink and to Prevent Re deposition of Ink to The Cellulose Fiber | 0.05 – 0.2 % | Mixture Of Non-Ionic Surfactants And Dispersants |
| Abstract Bio Deinking Liq | Improve pulp bleach ability and brightness, reduce dirt count | 0.02 – 0.05 % | Proprietary Formulation Comprised Of Various Enzymes And Necessary Surface Active Components |
Use of ABSTRACT-D AND ABSTRACT HD in Different Types of Verity of Paper.
| End Market | Furnish/Waste Fibre Type |
|---|---|
| Newsprint | Mixtures Of old newsprint (100%-40%) and magazines (0-60%) |
| Tissue | (A) chemical fibre and (B) predominantly chemical fibre |
| Printing/ Writing | (A) chemical fibre (B) mechanical fibre and (C) mixtures chemical fibre |
| Topliner | (A) chemical fibre |
| Testliner Chorma- Board | (A) mechanical fibre and (B) mixtures chemical fibre |
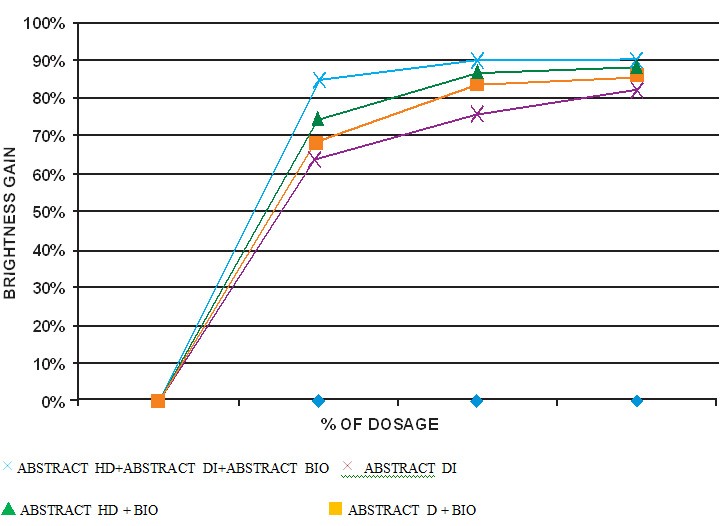
Figure 2: A line chart showing brightness gain against ink removal with different products of abstract deinking aid
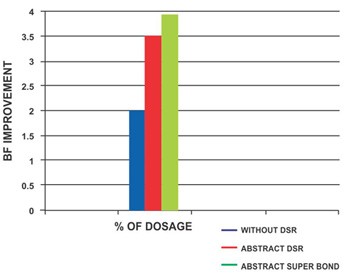
Dry Strength Resin
ABSTRACT’s dry strength programs offer papermakers another tool to manage end-product specifications, enhance operation profitability and develop new grades. The typical benefit of our dry strength program is improved strength properties and improved run ability. This gives you the option to increase machine speed, reduce basis weight, and to use lower cost fiber.
STRENGTHENING PROGRAMME
“Strengthening” should be used after Refining Machine Chest.
Primary Bonding mechanism responsible for Dry Strength involved the formation hydrogen bonds between Hydroxyl groups on adjacent fibers as water is removed from the shit.
Tensil`s strength in low density sheets determine by the number of fiber to fiber bond (crossover points). And the strength of individual fiber to fiber bond.
The use of “Super Bond” can improve compressed strength of individual fiber to fiber bonds through supplemental hydrogen bonding in areas of existing fiber crossovers.
| Product Name | Solid Content | Dosage | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abstract Suber Bond | 25+1 | 3-5 KG Added to the machine chest after refining. |
|
| Abstract DSR | 16+1 | 3-5 KGS Added to the machine chest after refining. |